Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwai, Naofumi; Kuribayashi, Toshihiro; Kawata, Norio
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2013/10
In order to support international safeguards activities conducted by the IAEA, the Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been providing the International Training Course on State Systems of Accounting for and Control of Nuclear Material (SSAC) targeted mainly at Asian nations as a Japan's subsidized project by making good use of Japan's efforts and experience in nonproliferation. The course provides the opportunity of a facility tour and an A-bombed site visit, as well as offers lectures and practical trainings necessary to build and maintain the SSAC for those including "government officials involved in safeguard policy and regulation" and "business operators engaged in accounting". This paper discusses the summary of the SSAC training course operation held at the ISCN.
Okazaki, Hiro; Sumi, Mika; Abe, Katsuo; Sato, Mitsuhiro; Kageyama, Tomio
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
The quality control section of Plutonium Fuel Development Center (PFDC) has been analyzing isotopic compositions by Mass Spectrometry as well as content by Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS) of plutonium and uranium in nuclear materials. Along with establishing and managing the quality assurance system, ensuring the reliability of the analysis data is important. PFDC has been establishing the quality management system with ISO 9001. We addressed technical improvement to improve further reliability of analysis quality, and accredited for ISO/IEC 17025 in March 2010. While ISO 9001 consists of management requirements for quality system of organizations, ISO/IEC 17025 consists of technical requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories in addition to the management requirements. In this presentation, we report our approaches to have accreditation and operation status for isotopic compositions and content of plutonium and uranium in nuclear materials.
Zaima, Naoki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Kado, Kazumi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 10 Pages, 2013/10
A uranium mass assay system for 200-litter wastes drums applied by NDA method was developed and accumulated the data of the actual uranium bearing wastes drums. The system consists of the 16 pieces of Helium-3 proportional counters for neutron detection generated from  U(
U( ,n) reaction or
,n) reaction or  U spontaneous fissions with polyethylene moderation and a Germanium solid state detector for
U spontaneous fissions with polyethylene moderation and a Germanium solid state detector for  ray detection as to determine uranium enrichment. In previous report, some measurement experiences had been introduced briefly. After that satisfactory works had been continued and the uranium determination data of 850 drums had been accumulated approximately. On the other hand considerable problems on the system had been revealed technically or analytically. Such experiences are to be described precisely, in addition newly gained knowledge will be marshaled. Furthermore the next improvement plans are now prepared that will be capable of active neutrons assay for uranium bearing wastes drums.
ray detection as to determine uranium enrichment. In previous report, some measurement experiences had been introduced briefly. After that satisfactory works had been continued and the uranium determination data of 850 drums had been accumulated approximately. On the other hand considerable problems on the system had been revealed technically or analytically. Such experiences are to be described precisely, in addition newly gained knowledge will be marshaled. Furthermore the next improvement plans are now prepared that will be capable of active neutrons assay for uranium bearing wastes drums.
Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao; Kurata, Noritaka; Kobayashi, Nozomi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; To, Kentaro; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
no abstracts in English
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; Kauwenberghs, K.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2013/10
We have no established methods to quantify the amount of nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel derived from a nuclear accident such as the one occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For this reason, neutron resonance densitometry, combining neutron resonance transmission analysis and neutron resonance capture analysis, is under development. It is expected that such debris have a wide variety of size, shape, and concentration of impurities. Experiments with the Neutron Resonance Transmisson Analysis (NRTA) using three Cu metal disks with different thickness of 0.125 mm, 0.25 mm, and 0.7 mm were made between November 2012 and February 2013 at the Geel Electron LINear Accelerator (GELINA) to investigate sample thickness effect on the transmission analysis. We experimentally derived the areal density for the individual Cu samples with the resonance shape analysis code REFIT, and then compared them with the declared areal density. It was found that the REFIT-evaluated areal density was consistent with declared ones for each sample.
Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Seya, Michio; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 6 Pages, 2013/10
Neutron resonance densitometry (NRD) has been proposed to quantify nuclear materials in particle-like debris of melted fuel formed in severe accidents of nuclear reactors such as Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. NRD is a method combining NRTA (neutron resonance transmission analysis) and NRCA (neutron resonance capture analysis). It relies on neutron TOF (time of flight) technique using a pulsed white neutron source. The use of a special  -ray spectrometer for NRCA and an evaluation of the achievable accuracy are discussed. The discussion is based on results of Monte Carlo simulations combined experimental data from measurements carried out at GELINA. In this contribution, progress made in the development of NRD for the characterization of nuclear materials mixed with highly radioactive nuclides is presented, together with the basic concept and principles.
-ray spectrometer for NRCA and an evaluation of the achievable accuracy are discussed. The discussion is based on results of Monte Carlo simulations combined experimental data from measurements carried out at GELINA. In this contribution, progress made in the development of NRD for the characterization of nuclear materials mixed with highly radioactive nuclides is presented, together with the basic concept and principles.
Nakajima, Shinji; Nagatani, Taketeru; Asano, Takashi; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; Kumakura, Shinichi*; Watanabe, Takehito*; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
The Advanced Verification for Inventory Sample System (AVIS) is a nondestructive assay (NDA) system in order to verify the plutonium mass in the small MOX samples at Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL) MOX fuel fabrication plant (J-MOX) under construction. The AVIS is required the high measurement performance because the AVIS will be used as a verification tool to substitute destructive analysis for a part of the samples which needs the bias defect verification. Therefore, the AVIS will fulfill an important role in the safeguards approach for J-MOX. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducted the performance test of the AVIS under the contract with NMCC. As the results of these tests, we confirmed that the AVIS could almost satisfy the required performance by IAEA.
Komeda, Masao; Ozu, Akira; Zaima, Naoki; Nakatsuka, Yoshiaki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Takase, Misao; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Kureta, Masatoshi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Takashi; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Endo, Yuji; Nakamura, Hironobu
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 8 Pages, 2013/10
no abstracts in English
Okumura, Yukiko
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 6 Pages, 2013/10
NPT obligates non-nuclear-weapon State Party to it to verify treaty compliance through safeguards and authorizes the IAEA to its implementation. In 1972, the Model Protocol of CSA was adopted. An new legal authority was required, however, when the shortcoming of the safeguards implementation was highlighted in early 1990s in Iraq. So as to confirm the non-existence of the undeclared nuclear material and nuclear activity the AP was adopted by the IAEA Board of Governors in 1997. In order to support international safeguards activities conducted by the IAEA, the ISCN of JAEA has been conducting international cooperation, through seminars and training courses, targeted mainly on Asian countries. We have been supporting the countries to enable the enhancement of ratification and effective implementation. This paper will be focusing on how ISCN is contributing to the Asian countries as well as the IAEA's infrastructure development support for safeguard implementation.
Noro, Naoko
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 7 Pages, 2013/10
This paper will briefly illustrate ISCN's achievement in the past years, and introduce challenges and measures of ISCN in nuclear security human resource capacity building assistance.
Hamada, Kazuko
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
The Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is promoting capacity building support internationally in the aras of nuclear nonproliferation and security. While this kind of capacity building support is accelerating, it is increasingly recognized that many challenges exist to achieve effective capacity building support, such as gaps between needs and support contents and possible redundancies in various support activities. As a result, the effectiveness of capacity building support is seriously questioned, and greater importance is now attached to the harmonization among support activities. This paper will introduce the concepts and approache of ISCN's capacity building support, discuss the challenges for this support to serve for enduring efforts toward the enhanvement of nuclear nonproliferation and security and possible ways to overcome these challenges.
Terao, Norichika; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
An equation for risk assessment in physical protection is shown by a probability of an adversary attack during a period time, 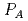 , a probability of system effectiveness,
, a probability of system effectiveness, 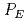 , and consequence value,
, and consequence value, 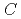 . In addition,
. In addition, 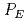 is shown as the multiplication of a probability of interruption of the facility,
is shown as the multiplication of a probability of interruption of the facility, 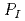 , by a probability of neutralization by response force,
, by a probability of neutralization by response force, 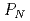 . In this study, it is assumed that an adversary assaults a hypothetical nuclear facility. The new quantification method about
. In this study, it is assumed that an adversary assaults a hypothetical nuclear facility. The new quantification method about 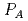 and
and 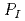 in risk evaluation formula is devised, and risk assessment is attempted. In case of
in risk evaluation formula is devised, and risk assessment is attempted. In case of 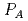 , the possibility of assaults against a nuclear facility is discussed by using terrorism data written in the open source database of terrorism, Global Terrorism database (GTD), summarized by University of Maryland. In addition, it is discussed about
, the possibility of assaults against a nuclear facility is discussed by using terrorism data written in the open source database of terrorism, Global Terrorism database (GTD), summarized by University of Maryland. In addition, it is discussed about 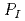 by using the way of thinking of a risk assessment tool, EASI, developed by the Sandia National Laboratories (SNL). In the hypothetical nuclear facility, the performance of response force, sensors, and communication is expressed quantitatively by probability distribution based on some assumptions.
by using the way of thinking of a risk assessment tool, EASI, developed by the Sandia National Laboratories (SNL). In the hypothetical nuclear facility, the performance of response force, sensors, and communication is expressed quantitatively by probability distribution based on some assumptions.
Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamura, Hironobu; Fujisaku, Sakae; Kurita, Tsutomu; LaFleur, A. M.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Marlow, J. B.*
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
In case of the Pu mass determination in scattered powder in a GB using Continuous Neutron Monitor (CNM) with totals, self-multiplication of neutron (M) and  value are properly required to be set. M can be easily estimated by a simulation code, but it is very difficult to estimate
value are properly required to be set. M can be easily estimated by a simulation code, but it is very difficult to estimate  value by such a simulation because interactions between
value by such a simulation because interactions between  ray generated from Pu and impurities are not consistent. Therefore, we tried to examine an estimation technique of
ray generated from Pu and impurities are not consistent. Therefore, we tried to examine an estimation technique of  value by direct measurement. As a result, by measuring the samples taken from the scattered powder using a multiplicity counter with a dual ring structure of He-3 tubes, we could confirm a good correlation between ring ratio (inner / outer ring count rates) and the
value by direct measurement. As a result, by measuring the samples taken from the scattered powder using a multiplicity counter with a dual ring structure of He-3 tubes, we could confirm a good correlation between ring ratio (inner / outer ring count rates) and the  values. Thus, we can estimate
values. Thus, we can estimate  value in the powder directly by the ring ratio measurement. By applying this technique to CNM and designing a new detector with a double layer structure of neutron detection tubes, we had a prospect that CNM would be able to measure the Pu mass continuously.
value in the powder directly by the ring ratio measurement. By applying this technique to CNM and designing a new detector with a double layer structure of neutron detection tubes, we had a prospect that CNM would be able to measure the Pu mass continuously.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Terao, Norichika
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
Nuclear security risk assessment with the Markov model applied to random events is performed to explore an evaluation methodology for physical protection in nuclear facilities. Because the security incidences are initiated by malicious and intentional acts, expert judgement and Bayes updating are used to estimate scenario and initiation likelihood, and it is assumed that the Markov model can be applied to incidence sequence
Kimura, Yoshiki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Funatake, Yoshio; Sato, Kaneaki; Toda, Nobufumi; Shinoda, Yoshiharu; Watahiki, Masaru; Kuno, Yusuke
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has initiated R&D project on nuclear forensics technology such as analytical technologies towards the establishment of nuclear forensics capabilities in Japan. National Nuclear Forensics Library (NNFL) is one of the fundamental nuclear forensics capabilities and a prototype NNFL has been developed as one R&D topic of the project at JAEA. Main objective of a NNFL is to determine whether a seized nuclear or other radioactive material from nuclear security event (e.g. illicit trafficking) is originated from a country or not. Analytical data of the seized material are compared with the existing materials populated in a NNFL, and its attributions such as origin and history will be identified. This paper describes the current status and future plan on the development of prototype NNFL. The outline and the results of the participation in an international table top exercise on NNFL named "Galaxy Serpent" were also reported in the present paper.
Kawakubo, Yoko; Inoue, Naoko; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is carrying out R&D to design and establish an Information-Sharing Framework (ISF) for supporting and promoting nuclear transparency in cooperation with Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), the Korean Institute for Nonproliferation and Control (KINAC), and Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI). Partner organizations have agreed on starting by establishing ISF with a focus on nuclear nonproliferation experts in Track II as primary information providers/receivers. Thus far, requirements for ISF have been developed for providing clear steps to design and establish ISF and ensuring its sustainability. As the next step, ISF is to be established following the requirements and demonstration of information sharing will be carried out. In the long-term, ISF could be expanded to invite other interested organizations and include other information. This paper describes the effort to design and establish ISF by focusing on the requirements which has been developed under the joint R&D.
Bolind, A.; Seya, Michio
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 10 Pages, 2013/10
This paper reports on the recent progress at JAEA concerning various R&D programs for advanced technologies for the measurement and detection of nuclear material for security and safeguards. These programs are being coordinated through the Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Nonproliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN). One program is the development of a neutron detector that uses a ZnS ceramic scintillator material instead of He-3 gas. JAEA is preparing to conduct benchmark experiments to compare the performance of an NDA system that uses the new scintillator detectors against the performance of the existing NDA system that uses He-3 detectors. The Nuclear Resonance Fluorescence (NRF) program is developing NRF as an NDA technique to detect and measure nuclear-material isotopes in used fuel assemblies and in melted nuclear fuel debris. The Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) program is similarly developing NRD to measure melted nuclear-fuel debris. This past year, JAEA has conducted several important NRF and NRD experiments, collaborated closely with international partners, and improved the NRF and NRD theories and computer-simulation codes. Lastly, JAEA has collaborated with Los Alamos National Laboratory to test a PNAR + SINRD NDA detector on used nuclear fuel assemblies at Fugen.
 -ray techniques for the non-destructive assay of used nuclear fuel assemblies
-ray techniques for the non-destructive assay of used nuclear fuel assembliesBolind, A.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 2 Pages, 2013/10
This paper proposes to combine two neutron-based NDA techniques and one  -ray NDA technique, to assay used LEU and HEU fuel assemblies. The two neutron techniques are the "passive neutron albedo reactivity" technique (PNAR) and the "
-ray NDA technique, to assay used LEU and HEU fuel assemblies. The two neutron techniques are the "passive neutron albedo reactivity" technique (PNAR) and the " Cf interrogation with prompt neutron detection" technique (CIPN). The
Cf interrogation with prompt neutron detection" technique (CIPN). The  -ray technique is a total
-ray technique is a total  -ray measurement. The two neutron techniques are combined through a mathematical model, while the incorporation of the
-ray measurement. The two neutron techniques are combined through a mathematical model, while the incorporation of the  -ray technique is empirical. By combining the measurements of three independent physical properties, the proposed method satisfies the requirements for a determinate solution of the isotopic content.
-ray technique is empirical. By combining the measurements of three independent physical properties, the proposed method satisfies the requirements for a determinate solution of the isotopic content.
Seya, Michio; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Iimura, Hideki; Kureta, Masatoshi; Takamine, Jun; Hajima, Ryoichi; Hayakawa, Takehito; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 10 Pages, 2013/10
The forming of MF in severe accidents of nuclear reactors such as Units 1 - 3 of Fukushima-Daiichi NPP (Nuclear Power Plant) inevitably change the category of the nuclear reactor from "item facility" to "bulk-handling facility". At removal of the MF it is necessary to break chunks of MF into relatively small blocks by using some tools, resulting in debris that consists of cut or small rock-like debris and particle (or grain)-like debris in bulk form. This paper presents a categorization of debris of MF and two possible non-destructive assay (NDA) technologies for precise measurement which could be applied to the NM accountancy of MF debris. One of them is Neutron Resonance Densitometry (NRD) for particle-like (or grain-like) debris, and another is NRF (Nuclear Resonance Fluorescence) NDA using LCS (Laser Compton Scattered)  -rays (mono-energetic
-rays (mono-energetic  -rays) for cut or small rock-like debris. The paper also describes about the recent development of these two technologies.
-rays) for cut or small rock-like debris. The paper also describes about the recent development of these two technologies.